- Published on
TypeScript + Vue3 Demo
- Authors
- Name
- DP Piggy
- @xiaozhudxiaozhu
1. Why Use TypeScript
- Type errots are caught at compile time (类型错误会在编译时被捕获)
- Richer Eidtor Support (autocompletion) (更丰富的编辑器支持,许多编辑器都支持使用 TypeScript, like vscode)
- Easier to read and understand the code (更容易阅读和理解代码)
- Better developer experience like debugging (更好的开发体验 debug)
2. create project
2.1 vue-cli
2.1.2 install vue-cli
# 全局卸载vue-cli
npm uninstall -g vue-cli
# 全局安装新版的vue-cli
npm install -g @vue/cli
# 查看vue-cli的版本
vue --version
2.1.3 create project
vue create ts-vue-demo
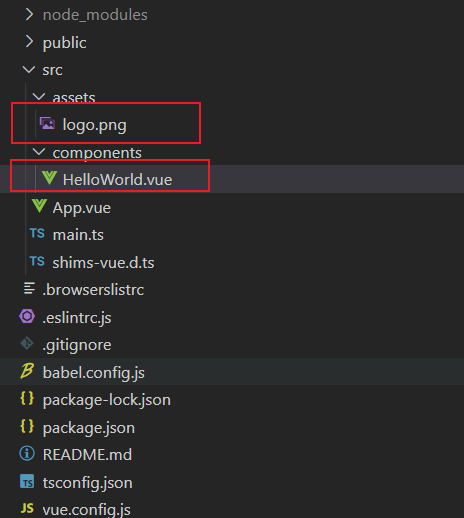
2.2 clean our project and run it
delete assets/logo.png and components/HelloWorld.vue (we don' t need these files)
enter App.vue and delete the following code
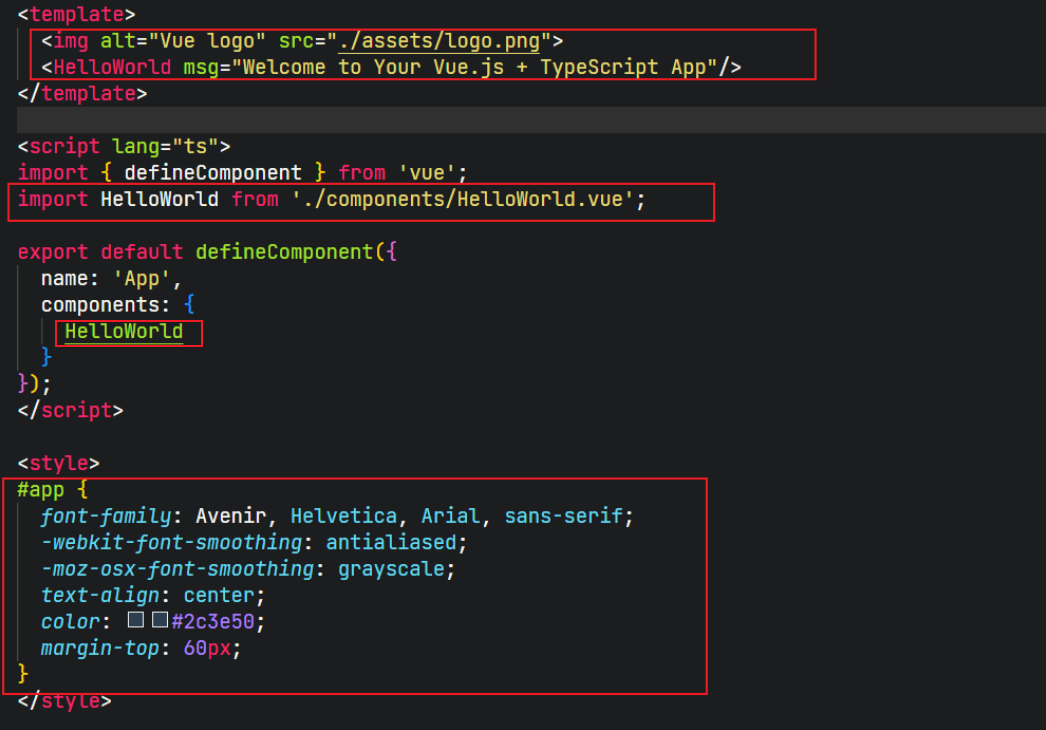
create a global.css file under assets dir
@import url('https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Open+Sans:wght@300;400;600;700&display=swap');
body {
font-family: 'Open Sans';
background: #ece6d9;
}
and then import this in main.ts
import './assets/global.css'
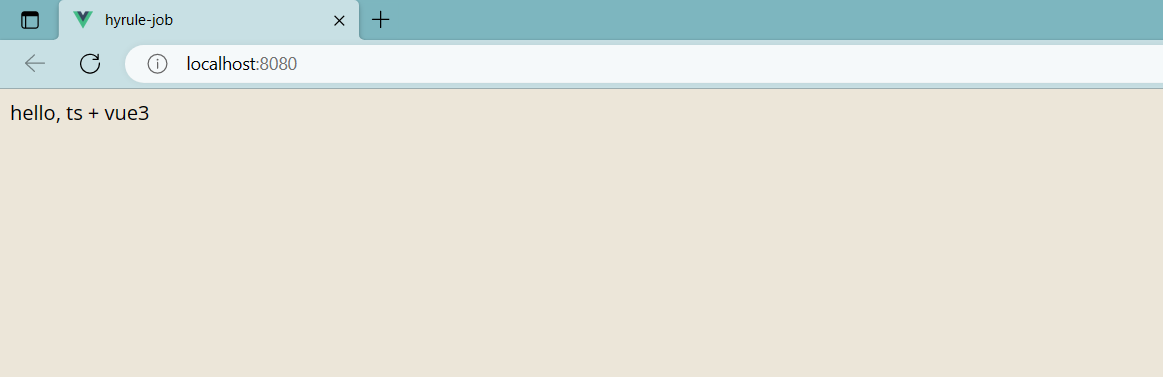
use the following command to run our project
npm run serve
If you see this, you have completed the initial creation of the project
3. learning
3.1 use options api
3.1.1 experience ts
the following example use option api
specify property name type as string, we can not change it
<template>
<div id="app">
{{ name }}
<!--if fill the param with a number, error -->
<button @click="changeName('xiaozhu')">
change name
</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: {},
data() {
return {
// Ts inferred this type to be a string, because 'Link'
// So we can not change name into number in futrue
name: 'Link'
}
},
methods: {
// we should specify the param type as string
// if we sepcify the param type as number , error
changeName(name: string) {
this.name = name
}
}
});
</script>
<style>
</style>
Now we add a new property : age. we want the age to a number. However, we also want to allow the age property to be a string type in the future. We can achieve this by following the way.
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ name }} - {{ age }}</p>
<!--if fill the param with a number, error -->
<br/>
<button @click="changeName('xiaozhu')">
change name
</button>
<br/>
<button @click="changeAgeNumber(21)">
change age(number)
</button>
<br/>
<button @click="changeAgeString('100')">
change age(string)
</button>
<br/>
<button @click="changeAge(120)">
change age(number | string)
</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: {},
data() {
return {
// Ts inferred this type to be a string, because 'Link'
// So we can not change name into number in futrue
name: 'xiaoduoge',
// This means that age property can be string or number
age: 25 as number | string
}
},
methods: {
// we should specify the param type as string
// if we sepcify the param type as number , error
changeName(name: string) {
this.name = name
},
// if we add boolean, error
// we return and find the age type is specified as number | st
changeAge(age: number | string) {
this.age = age
return age
},
changeAgeNumber(age: number) {
this.age = age
return age
},
changeAgeString(age: string) {
this.age = age
return age
}
}
});
</script>
<style>
</style>
3.2 use composition api
3.2.1 reactive
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ name }} - {{ age }}</p>
<!--if fill the param with a number, error -->
<br />
<button @click="changeName('xiaozhu')">change name</button>
<br />
<button @click="changeAgeNumber(21)">change age(number)</button>
<br />
<button @click="changeAgeString('100')">change age(string)</button>
<br />
<button @click="changeAge(120)">change age(number | string)</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, reactive, toRefs } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: {},
setup() {
const state = reactive({
name: "xiaoduoge",
age: 25 as string | number,
});
return { ...toRefs(state) };
},
methods: {
// we should specify the param type as string
// if we sepcify the param type as number , error
changeName(name: string) {
this.name = name;
},
// if we add boolean, error
changeAge(age: number | string) {
this.age = age;
return age;
},
changeAgeNumber(age: number) {
this.age = age;
return age;
},
changeAgeString(age: string) {
this.age = age;
return age;
},
},
});
</script>
<style>
</style>
3.2.2 ref
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ name }} - {{ age }}</p>
<!--if fill the param with a number, error -->
<br />
<button @click="changeName('xiaozhu')">change name</button>
<br />
<button @click="changeAgeNumber(21)">change age(number)</button>
<br />
<button @click="changeAgeString('100')">change age(string)</button>
<br />
<button @click="changeAge(120)">change age(number | string)</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: {},
// setup() {
// const state = reactive({
// name: "xiaoduoge",
// age: 25 as string | number,
// });
// return { ...toRefs(state) };
// },
setup() {
const name = ref("xiaoduoge");
const age = ref<number | string>(25);
return { name, age };
},
methods: {
// we should specify the param type as string
// if we sepcify the param type as number , error
changeName(name: string) {
this.name = name;
},
// if we add boolean, error
changeAge(age: number | string) {
this.age = age;
return age;
},
changeAgeNumber(age: number) {
this.age = age;
return age;
},
changeAgeString(age: string) {
this.age = age;
return age;
},
},
});
</script>
<style>
</style>
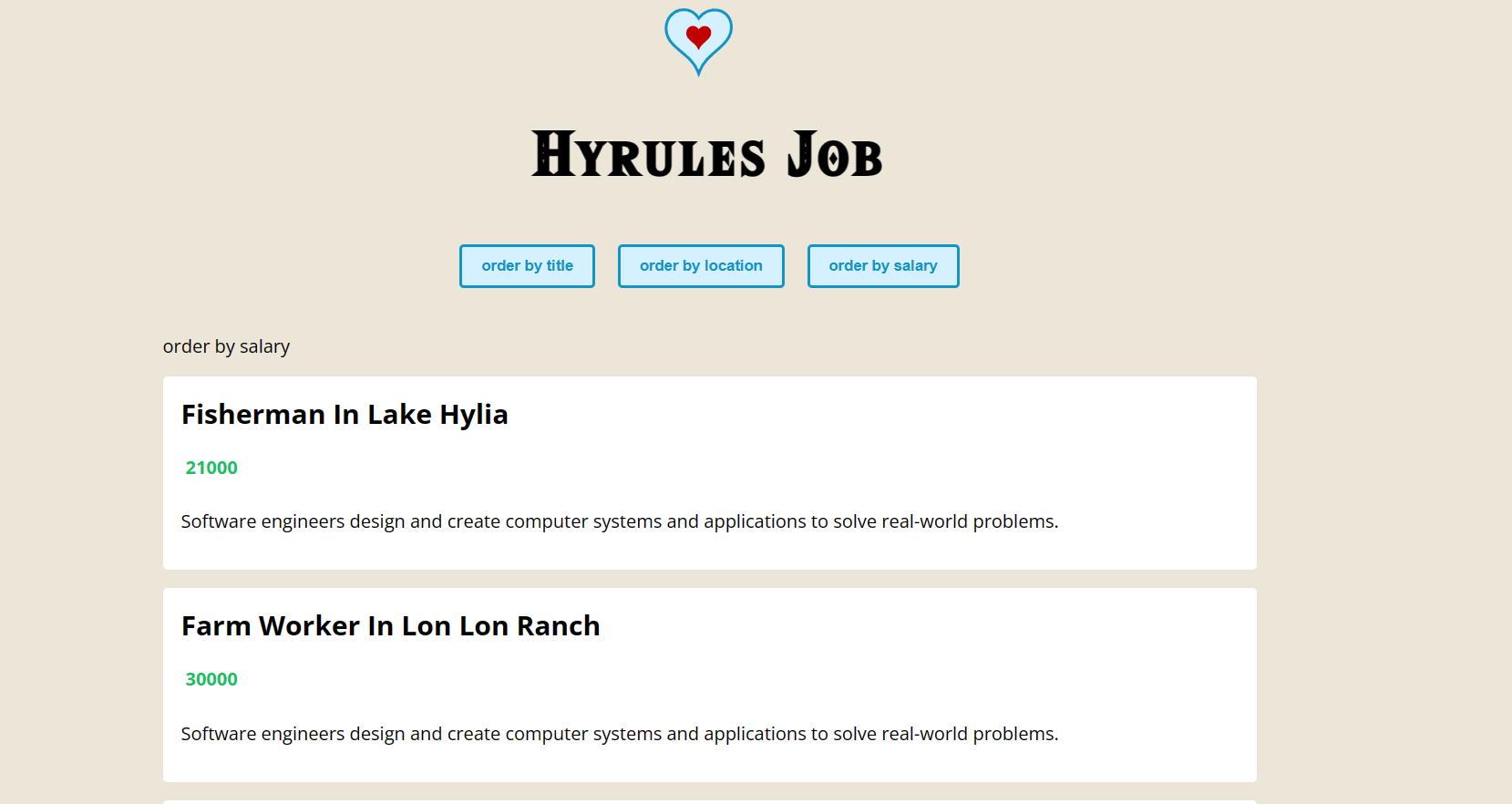
3.3 start the demo
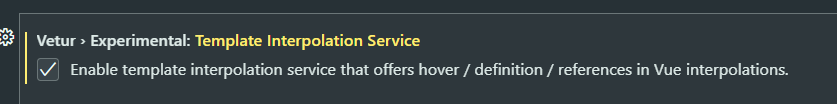
First of all, we should make sure that vetur template is checked
make a file "JobList.vue" in "compoents" dir
just write "ts", we can choose the ts template
JobList.vue
<template>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
and we should import JobList in App.vue
import JobList from './components/JobList.vue'
register component
components: {JobList},
<JobList :jobs="jobs"/>
Job.ts
interface Job {
title: string
location: string
salary: number
id: string
}
export default Job
JobList.vue
<template>
<div class="job-list">
<ul>
<!--we should make sure vetur template is checked -->
<!--if we don' t specify the job type, we cannot use job id -->
<li v-for="job in jobs" :key="job.id">
<h2>{{ job.title }} in {{ job.location }}</h2>
<div class="salary">
<p>
{{ job.salary }}
</p>
</div>
<div class="description">
<p>
Software engineers design and create computer systems and
applications to solve real-world problems.
</p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, PropType } from "vue";
import Job from "@/types/Job";
export default defineComponent({
props: {
jobs: {
// it is necessary
required: true,
// the prop type is Job[], and we should import
type: Array as PropType<Job[]>,
},
},
});
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<JobList :jobs="jobs"/>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue";
import Job from "@/types/Job";
import JobList from './components/JobList.vue'
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: {JobList},
setup() {
const jobs = ref<Job[]>([
{
title: "farm worker",
location: "lon lon ranch",
salary: 30000,
id: "1",
},
{
title: "quarryman",
location: "death mountain",
salary: 40000,
id: "2",
},
{
title: "flute player",
location: "the lost woods",
salary: 35000,
id: "3",
},
{ title: "fisherman", location: "lake hylia", salary: 21000, id: "4" },
{
title: "prison guard",
location: "gerudo valley",
salary: 32000,
id: "5",
},
]);
return { jobs };
},
methods: {},
});
</script>
<style>
</style>
3.4 functions
OrderTerm.ts
type OrderTerm = 'title' | 'salary' | 'location'
export default OrderTerm
JobList.vue
<template>
<div class="job-list">
<ul>
<!--we should make sure vetur template is checked -->
<!--if we don' t specify the job type, we cannot use job id -->
<li v-for="job in jobs" :key="job.id">
<h2>{{ job.title }} in {{ job.location }}</h2>
<div class="salary">
<p>
{{ job.salary }}
</p>
</div>
<div class="description">
<p>
Software engineers design and create computer systems and
applications to solve real-world problems.
</p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, PropType } from "vue";
import Job from "@/types/Job";
import OrderTerm from "@/types/OrderTerm";
export default defineComponent({
props: {
jobs: {
// it is necessary
required: true,
// the prop type is Job[], and we should import
// the type is js type, and we specify as ts type
type: Array as PropType<Job[]>,
},
order: {
required: true,
type: String as PropType<OrderTerm>
}
},
});
</script>
<style scoped>
.job-list {
max-width: 960px;
margin: 40px auto;
}
.job-list ul {
padding: 0;
}
.job-list li {
list-style-type: none;
background: white;
padding: 16px;
margin: 16px 0;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.job-list h2 {
margin: 0 0 10px;
text-transform: capitalize;
}
.salary {
display: flex;
}
.salary img {
width: 30px;
}
.salary p {
color: #17bf66;
font-weight: bold;
margin: 10px 4px;
}
</style>
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<header>
<div class="order">
<button @click="handleClick('title')">order by title</button>
<!-- if we change location to locations, error -->
<button @click="handleClick('location')">order by location</button>
<button @click="handleClick('salary')">order by salary</button>
</div>
</header>
<JobList :jobs="jobs" :order="order" />
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue";
import Job from "@/types/Job";
import OrderTerm from "./types/OrderTerm";
import JobList from "./components/JobList.vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: { JobList },
setup() {
const jobs = ref<Job[]>([
{
title: "farm worker",
location: "lon lon ranch",
salary: 30000,
id: "1",
},
{
title: "quarryman",
location: "death mountain",
salary: 40000,
id: "2",
},
{
title: "flute player",
location: "the lost woods",
salary: 35000,
id: "3",
},
{ title: "fisherman", location: "lake hylia", salary: 21000, id: "4" },
{
title: "prison guard",
location: "gerudo valley",
salary: 32000,
id: "5",
},
]);
// default order is title
const order = ref<OrderTerm>("title");
// specify the term type is OrderTerm and we shoule import
const handleClick = (term: OrderTerm) => {
order.value = term;
};
// don' t forget to return
return { jobs, handleClick, order };
},
});
</script>
<style>
header {
text-align: center;
}
header .order {
margin-top: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 10px;
color: #1195c9;
border: 3px solid #1195c9;
background: #d5f0ff;
padding: 8px 16px;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
3.5 computed
<template>
<div class="job-list">
<p>order by {{ order }}</p>
<ul>
<!--we should make sure vetur template is checked -->
<!--if we don' t specify the job type, we cannot use job id -->
<!--because we computed jobs and return orderedJobs, so we can use it -->
<li v-for="job in orderedJobs" :key="job.id">
<h2>{{ job.title }} in {{ job.location }}</h2>
<div class="salary">
<p>
{{ job.salary }}
</p>
</div>
<div class="description">
<p>
Software engineers design and create computer systems and
applications to solve real-world problems.
</p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { computed, defineComponent, PropType } from "vue";
import Job from "@/types/Job";
import OrderTerm from "@/types/OrderTerm";
export default defineComponent({
props: {
jobs: {
// it is necessary
required: true,
// the prop type is Job[], and we should import
// the type is js type, and we specify as ts type
type: Array as PropType<Job[]>,
},
order: {
required: true,
type: String as PropType<OrderTerm>,
},
},
// why use ...
// In Vue 3, you can use the prefix ... to destructure properties.
setup(props) {
const orderedJobs = computed(() => {
return [...props.jobs].sort((a: Job, b: Job) => {
return a[props.order] > b[props.order] ? 1 : -1;
});
});
return { orderedJobs };
},
});
</script>
3.5.1 Why we use "[...props.jobs]" ?
The destructuring syntax allows you to split the properties or elements of an object or array into separate variables. This is often convenient, for example when you need to assign the properties of an object to multiple variables.
In this example, you use destructuring syntax to destructure the props.jobs array into a separate array variable [...props.jobs]. This means that each element of the props.jobs array will be split into a separate variable.
The reason for doing this is that, in JavaScript, arrays are reference types. This means that if you perform operations on an array, you will directly modify the original array. To avoid this, you can use destructuring syntax to split the array into separate variables, thereby avoiding modifying the original array directly.
3.5.2 why we use "a[props.order] > b[props.order]" ?
In this example, the criterion for comparison is the value of a certain property of the object. The name of this property is passed in through props.order.
For example, if the value of props.order is 'title', then the sorting function will sort the objects based on their title property. Therefore, the comparison statement would become a.title > b.title.
The square bracket syntax [props.order] allows for dynamic access to an object's property. This way, when the value of props.order changes, the property being compared will also change.
The final result